|
Baker’s Yeast Can Survive Mars-like Stress Conditions, New Study Shows
Oct 14, 2025 by News Staff
« Previous |Next »
Exploring the possibility of the survival of life under extraterrestrial conditions is an important goal of astrobiology. In a new study, scientists used baker’s yeast, a powerful model organism, to assess the impact of Mars-like conditions; they observed that yeast survive shock waves and perchlorate treatment — two stressors relevant to Mars; further, yeast responds to Martian conditions by assembling conserved RNA-protein complexes.
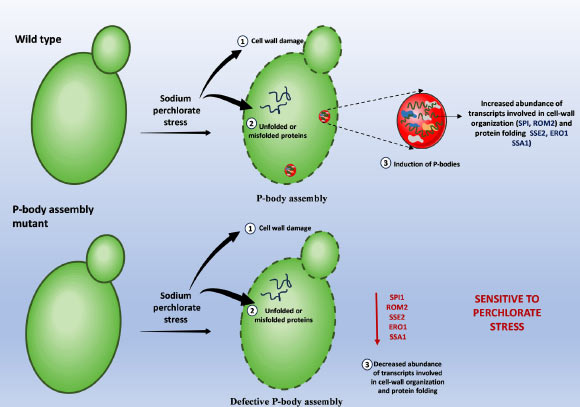
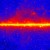
Model depicting the importance of RNP condensate in mediating survival under Mars-like stress condition. Image credit: Dhage et al., doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf300. “With advances in space science and astrobiology, exploring the potential of Mars in supporting life forms is gaining significant attention,” said Indian Institute of Science’s Dr. Purusharth Rajyaguru and colleagues. “Mars offers a range of hostile environmental conditions that a potential life form would need to overcome.” “Thus, understanding its unique and challenging environmental conditions becomes important.” “Martian stress conditions are characterized by the following: (i) high-intensity shock waves resulting from meteorite impacts, (ii) extreme temperature and pressure fluctuations, (iii) ionizing and solar UV radiations due to a thin atmosphere, and (iv) chaotropic agents like perchlorates.” “These conditions pose a serious obstacle to the survival of potential life forms.” In the study, the authors subjected Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is a widely used model yeast, to shock waves and perchlorates. They chose the yeast in part because it has already been studied in space. When stressed, yeast, humans, and many other organisms form ribonucleoprotein (RNP) condensates, structures made of RNA and proteins that protect RNA and affect the fates of mRNAs. When the stressor passes, the RNP condensates, which include subtypes known as stress granules and P-bodies, disassemble. Yeast exposed to 5.6 Mach intensity shock waves survived with slowed growth, as did yeast subjected to 100 mM sodium salt of perchlorate (NaClO4) — a concentration similar to that in Martian soils. Yeast cells also survived exposure to the combined stress of shock waves and perchlorate stress. According to the team, in both cases, the yeast assembled RNP condensates. Shock waves induced the assembly of stress granules and P-bodies; perchlorate caused yeast to make P-bodies but not stress granules. Mutants incapable of assembling RNP condensates were poor at surviving the Martian stress condition. Transcriptome analysis identified specific RNA transcripts perturbed by Mars-like conditions. “The results show the importance of yeast and RNP condensates in understanding the effects of Martian conditions on life,” the scientists concluded. Their paper appears today in the journal PNAS Nexus. _____ Riya Dhage et al. 2025. Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) condensates modulate survival in response to Mars-like stress conditions. PNAS Nexus 4 (10): pgaf300; doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf300
Published in
Tagged as
You Might Like
Share This Page
Latest News
Fossil of Carnivorous ‘Swamp Monster’ Found in BrazilOct 24, 2025 | Paleontology
Two New Specimens of Edmontosaurus annectens Preserve Fine Details of Scales and HoovesOct 23, 2025 | Paleontology
Latest Cretaceous Dinosaurs Lived in Vibrant, Regionally Distinct CommunitiesOct 23, 2025 | Paleontology
Super-Earth Candidate Found in Habitable Zone of Gliese 251Oct 23, 2025 | Astronomy
Australia’s First Peoples Were Fossil Collectors, New Study SuggestsOct 22, 2025 | Paleontology
Cosmic ‘Knots’ May Have Briefly Dominated Newborn Universe, Physicists SayOct 22, 2025 | Astronomy
New Research Reveals How Reptiles ‘Package Up and Pee’ Crystalline WasteOct 22, 2025 | Biology
ALMA Captures Spiral-Shaped Gas Streamer Guided by Magnetic Fields in Star-Forming RegionOct 21, 2025 | Astronomy
Total Solar Eclipses Can Trigger Dawn Behavior in Birds, Scientists SayOct 21, 2025 | Astronomy
Astronomers Directly Image Brown Dwarf around Nearby Red Dwarf StarOct 21, 2025 | Astronomy
Unexpected Mixture of Hydrogen Cyanide and Hydrocarbons May Exist on Saturn’s Moon TitanOct 21, 2025 | Planetary Science
Paranthropus boisei was Capable of Tool Making, New Fossil SuggestsOct 21, 2025 | Anthropology
New Species of Dome-Headed Dinosaur Identified in MontanaOct 20, 2025 | Paleontology
Lead Exposure May Have Influenced Evolution of Human Brain, Behavior, and Development of LanguageOct 20, 2025 | Anthropology
Milky Way’s Galactic Center Excess is Due to Dark Matter Annihilation: StudyOct 20, 2025 | Astronomy
Humans Evolved from African Ape-Like Ancestor, Research SuggestsOct 20, 2025 | Anthropology
Hubble Space Telescope Observes NGC 3370Oct 20, 2025 | Astronomy
New Species of Hawk-Cuckoo Discovered in BorneoOct 17, 2025 | Biology
ALMA Detects Heavy Water in Planet-Forming Disk around Distant ProtostarOct 17, 2025 | Astronomy
Paleontologists Discover New Species of Triassic Long-Necked DinosaurOct 16, 2025 | Paleontology
New Species of Triassic Carnivorous Dinosaur Identified in ArgentinaOct 15, 2025 | Paleontology
New Form of Ice Discovered: Ice XXIOct 15, 2025 | Physical Chemistry
Cardamom Seed Extract Can Enhance Production of Antiviral Proteins, Study SaysOct 14, 2025 | Medicine
Martian ‘Linear Dune Gullies’ are Created by Sliding Blocks of Carbon Dioxide Ice, Researchers FindOct 14, 2025 | Planetary Science
Europe’s Longest Sauropod Dinosaur Trackway Unearthed in EnglandOct 14, 2025 | Paleontology (责任编辑:) |